The Effect of Supply Chain Issues on Global Commerce and How to Respond
October 3, 2024 - Emily Newton
Revolutionized is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Learn more here.
Unraveling the cause and effect of supply chain issues on global commerce presents a multifaceted challenge. A single disruption almost always creates a ripple effect impacting every link in the chain, from manufacturing to last-mile delivery.
From automotive to electronics to pharmaceuticals, businesses grapple with the fallout of delays, shortages, and logistical challenges that threaten their bottom lines. The interconnectedness of modern logistics networks magnifies these repercussions, highlighting the need for proactive risk management and contingency planning to prevent widespread crises.
As stakeholders navigate the evolving economy, it’s critical to understand the impacts of faltering supply chains on global trade and what to do about it.
What’s Behind Supply Chain Issues in 2024?
Strains in global production networks started to emerge in late 2020, following a harrowing year of pandemic-induced lockdowns. The decline and subsequent recovery in economic activity catalyzed massive shifts in demand and supply that rocked the entire supply chain infrastructure.
Keep in mind these events occurred at a time of considerable monetary and fiscal stimulus, meaning people had cash to spend but fewer goods to purchase. Faced with an unprecedented surge in demand, suppliers worldwide struggled to meet the increase in orders. The World Trade Organization reported a 5.3% drop in global commerce that year, underlining the scale of the crisis. These set in motion the multiple issues plaguing the sector in 2024.
The Red Sea Crisis
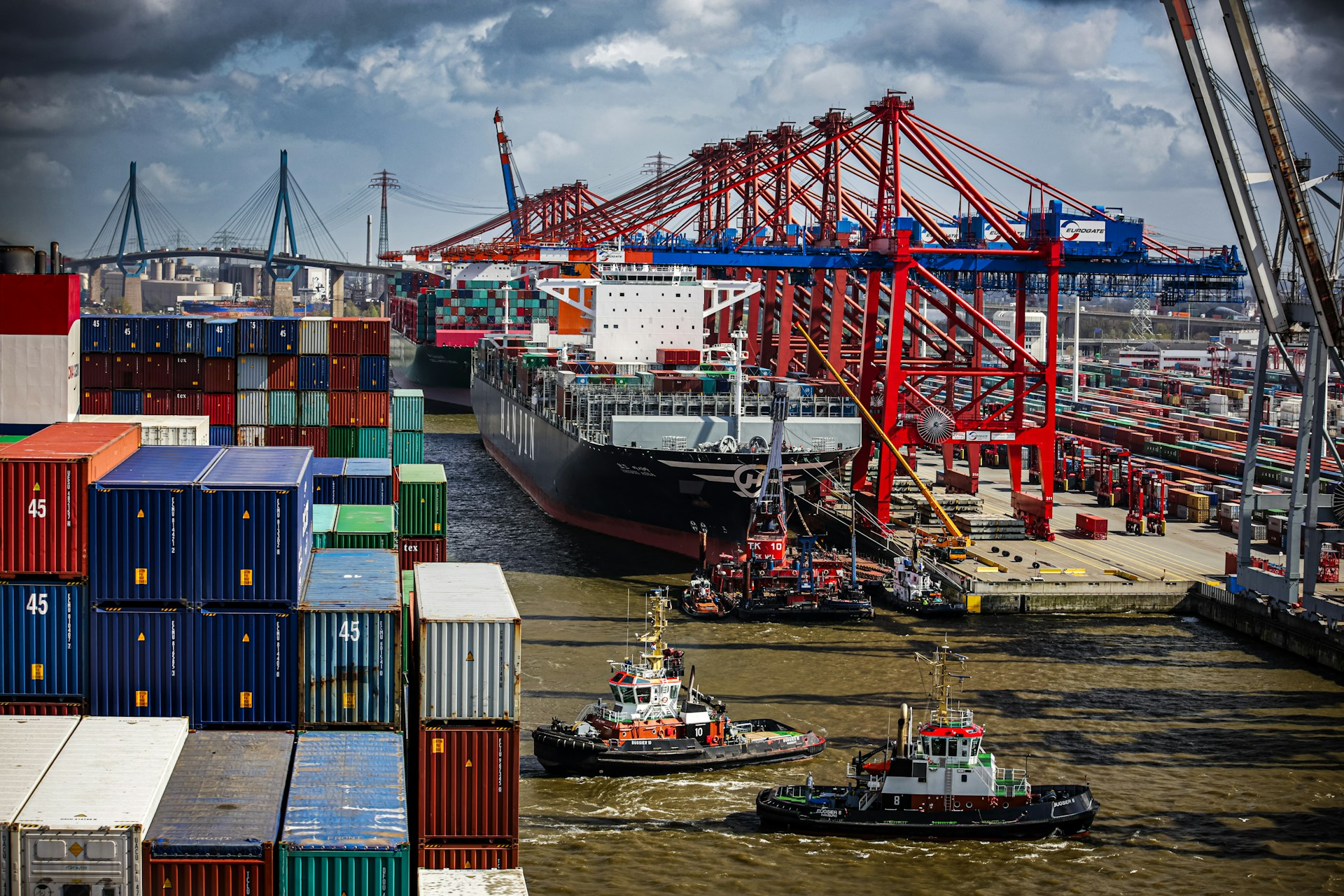
Maritime shipping is the cornerstone of international commerce. The Red Sea is a critical route within this network, transiting 30% of container shipments, primarily between Europe and Asia. This passage has recently become a hot spot for violent attacks by Houthi militants operating out of Yemen and neighboring regions.
These disruptions cause companies to pause or reroute their operations around the Cape of Good Hope, significantly impacting global trade and economic stability. For one, the journey can add up to 17 days to the transit time, costing an extra $1 million per trip for fuel.
Taiwan’s Semiconductor Situation
Geopolitical conflicts in Southeast Asia caused massive disruptions in Taiwan’s semiconductor factories, resulting in an acute shortage of microchips and related components. This scarcity affected just about every industry, costing the U.S. economy an estimated $240 billion in 2021.
The rapid adoption of technologies such as 5G, artificial intelligence, and electric vehicles heightened the need for semiconductors. This surge in demand outstripped existing supply capabilities.
How Do These Disruptions Impact Worldwide Trade?
The most critical effect of supply chain issues on global commerce is the disruption to the flow of goods and services — leading to delays in production, distribution and delivery. These disruptions can have cascading effects on businesses, consumers and the economy as a whole.
1. Increased Costs and Inflation
Supply chain problems often lead to increased production and shipping costs, which have been steadily growing in recent years. For example, freight indexes have risen nearly 10 times higher than pre-pandemic rates.
As companies face delays and shortages, they pay higher prices for raw materials and components, which are passed on to consumers. This contributes to inflation, affecting purchasing power and overall economic stability.
2. Production Delays and Reduced Output
Manufacturers reliant on global supply chains have faced significant delays due to shortages of essential components or raw materials. The automotive industry is a prime example.
Automakers like Ford and General Motors announced production cuts due to semiconductor shortages. Ford reported a loss of about $2.5 billion in earnings in 2021 because of these disruptions. As a result, consumer wait times for new vehicles extended significantly, with some models taking months or even over a year to become available.
3. Market Volatility
Supply chain disruptions contribute to market volatility as investors react to uncertainties. For example, major stock indices like the S&P 500 and Dow Jones experience sharp declines due to fears surrounding global trade interruptions and economic shutdowns. Companies may struggle to forecast demand accurately when logistics networks are unstable, causing fluctuations in their stock values as investors react to potential risks and challenges.
4. Shifts in Consumer Behavior
As product availability fluctuates, consumer behavior can change dramatically. Shortages may drive consumers to seek alternatives or delay purchases, impacting brand loyalty and long-term sales strategies. For example, consumers might turn to competitors or substitute products if a popular electronic device is unavailable, with far-reaching ramifications for local and international commerce.
How to Respond to Supply Chain Disruptions
Businesses must navigate the onslaught of financial and operational bottlenecks brought about by long-standing supply chain issues. These innovative strategies and practices can help mitigate risks and bypass these hurdles.
Digital Transformation
Technological advancements in AI, the Internet of Things (IoT) and blockchain are transforming the supply chain landscape, introducing increased resilience through digital automation. For example, AI-powered predictive analytics can enable companies to foresee potential disruptions and automatically adjust inventory to minimize overstock and stockouts.
Supplier Diversification
One of the most effective ways to mitigate supply chain risks is diversifying suppliers across different regions. This reduces reliance on a single source and minimizes the impact of localized disruptions. Since the COVID-19 pandemic, several companies, including Apple, Samsung and Adidas, realized the risks of relying heavily on Chinese manufacturing and shifted some production to neighboring Vietnam and India.
Reshoring and Nearshoring
Reshoring (bringing production back to the home country) or nearshoring (moving production closer to the home market) can reduce dependency on distant suppliers and minimize transportation delays.
These measures set the stage for the now famous “Made in America, for America” slogan used by politicians canvassing votes. A 2021 Kearney report found that 92% of U.S. manufacturing executives considered reshoring or nearshoring due to supply chain disruptions caused by the pandemic.
Strategic Stockpiling
Maintaining higher inventory levels can buffer against supply chain disruptions. While this approach ties up capital, it ensures companies can meet customer demand during shortages.
Mitigate the Effect of Supply Chain Issues on Global Commerce
Without question, logistics challenges place considerable strain on global trade with extensive impacts on local economies. One thing is clear — conventional supply chain management patterns are evolving and companies must adapt accordingly or risk falling behind for good. Technological solutions and innovative practices will ensure resilient supply chains to meet future demand.
Revolutionized is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Learn more here.
Author
Emily Newton
Emily Newton is a technology and industrial journalist and the Editor in Chief of Revolutionized. She manages the sites publishing schedule, SEO optimization and content strategy. Emily enjoys writing and researching articles about how technology is changing every industry. When she isn't working, Emily enjoys playing video games or curling up with a good book.